
A bridge spanning the river Vltava and connecting Holešovice and Libeň. A unique 1920s avant-garde functionalist building.

Iron and concrete fortifications, the most numerous structures of the Czechoslovak interwar defence system. Many of them are now a popular tourist sight and an important place of remembrance.

Battle vehicle designed by engineer František Zubatý and manufactured by Škoda between 1938 and 1939. It was the main battle tank of the Czechoslovak army between the two wars.

An exceptionally successful tank manufactured by the ČKD in the late 1930s and designed by Alexei Surin. Owing to its balanced characteristics and exceptional reliability, it is regarded as one of the best tanks of the early stages of the Second World War.

Czech actor and Czech-American film director and producer, oceanologist, ecologist and writer.

The second post-war hydroelectric power station, a part of the Vltava cascade and the largest artificial lake in the Czech Republic.

Diesel electric locomotive first built in 1964, intended for passenger, express and light cargo trains. Owing to its universal purpose, it is in service on both national and regional lines.

Identification marking of Czech locomotives valid since 1 January 1988. It was preceded by the so-called Kryšpín's locomotive identification marking. In 2006 it was complemented with another, European identification marking.

A bridge built in 1999 to replace several bridges that had existed there from 1369.

The first private Czech scientific satellite. It serves as a space laboratory for new types of electronic components intended for use in future satellites.

The first Czechoslovak satellite launched into space and also the first of five microsatellites of the Czechoslovak, later Czech space programme.

The second Czechoslovak satellite. It is now defunct, although still in orbit around Earth.
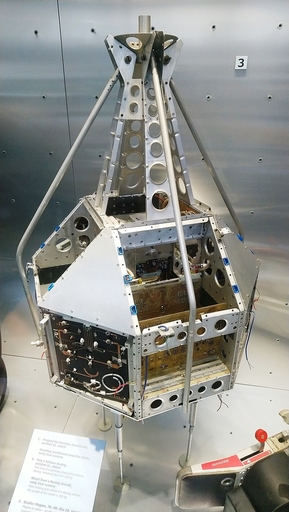
Czechoslovak satellite built for studying the magnetosphere. It was launched in 1991 and it investigated the density of the ionosphere in order to allow for more accurate forecasts of magnetic storms.

The first satellite built by the independent Czech Republic. It was launched in 1995. Its mission was to determine the speed of movement of magnetopause and to investigate other optical phenomenon in the Earth’s atmosphere.

The fifth and last of the Magion satellites. Its mission was to measure the Earth’s magnetic field, the electric field around the satellite and plasma waves, to observe Aurora Borealis and the intensity, temperature and density of charged particles and measure the precise lengths of the Solar cycle.

Austrian physicist and philosopher from Moravia. He was the dean and rector of Charles-Ferdinand University in Prague. He established important principles of optics, mechanics and the dynamics of waves.

Czechoslovak machine pistol manufactured in the 1960s. It is famous as an exceptionally light and compact weapon, ideal for use by members of security forces and special units.

The tenth bridge spanning the river Vltava in Prague, connecting the Old Town and the Lesser Quarter. It was named after painter Josef Mánes and is one of the few bridges built in Czech Cubist style.
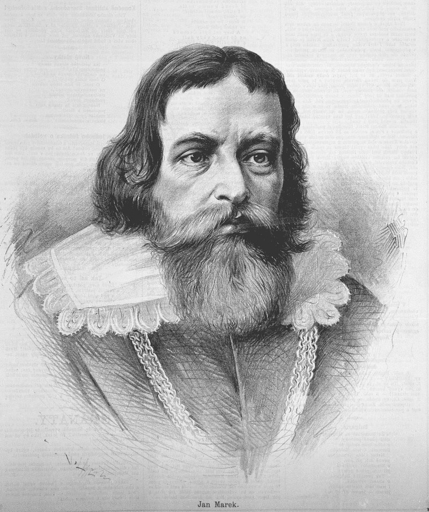

Prominent Czech polyhistorian, scientist, physician, physicist, mathematician, astronomer and philosopher of the era after the Battle of White Mountain, nicknamed “Prague Hippocrates”, “Bohemian Galileo Galilei”, “Bohemian Plato” and “Archimedes from Landskron”. He discovered the dispersion of light and was the first to write about the wave-line nature of light.
2016-2020 ABCzech.cz - © Filozofická fakulta Univerzity Karlovy
Content from this website may be used without permission only for personal and non-commercial purposes and with the source cited. Any other use is allowed only with the authors' consent.
This web application Sonic.cgi meets GDPR requirements. Current information can be found here.